Creating Effective Home-Based Care Systems in a Value-Based World
Healthcare is at an inflection point. As value-based care models reshape the economic landscape, a fundamental shift is occurring in how and where care is delivered. Healthcare policy expert Terry Sullivan recently articulated this transformation during a discussion about value-based care strategies: the recognition that traditional facility-centric models must evolve to meet the demands of modern healthcare economics and patient preferences.
The numbers tell a compelling story. Within the over-65 population, 55.8 million live at home, and the remaining 2.3% (1.3 million) live in nursing homes. Add in assisted living facilities, and you can add 818,800 elderly Americans to that count. By 2060, that 55.8 million is expected to increase to 95 million.
As value-based care reshapes healthcare economics, organizations are recognizing that home-based care isn’t just a patient preference—it’s an economic and clinical necessity for enhancing care and creating a sustainable model.
Let’s examine why this shift is happening, how technology enables it, and what healthcare organizations need to consider as they develop home-based care strategies.

Dr. Sullivan is an internist and public health physician. He served for a decade as the Chair of the Colorado Board of Health. He has been a regional CMO for multiple MCOs, including the Colorado Blues and Humana. For the last 10 years, Dr. Sullivan has focused on all aspects of the Post Acute marketplace, with an emphasis on advanced technology assessment, utilization, and reimbursement. He currently serves as a consultant for Neteera
Evolving Beyond Traditional Care Models
For decades, the American healthcare system has revolved around hospitals as both care delivery hubs and economic centers. However, this approach presents some challenges:
Financial inefficiency: “Hospitals receive more than 31% of the money. Yet the perception of their value is limited,” Sullivan notes. “Operational inefficiencies and rising costs are impacting this view.”
Misaligned incentives: Payment models need to adapt to align with outcome-focused reimbursement structures.
Fragmented care: Home-based care creates opportunities to bridge episodes seen as isolated episodes and provide more continuous patient engagement.
Patient preference: Most patients—particularly older adults with chronic conditions—prefer to receive care at home when possible.
As payment models shift toward value-based care, healthcare systems need to adapt their strategies to align with outcome-focused structures. The goal for hospitals is to integrate home-based services while maintaining core acute care excellence.
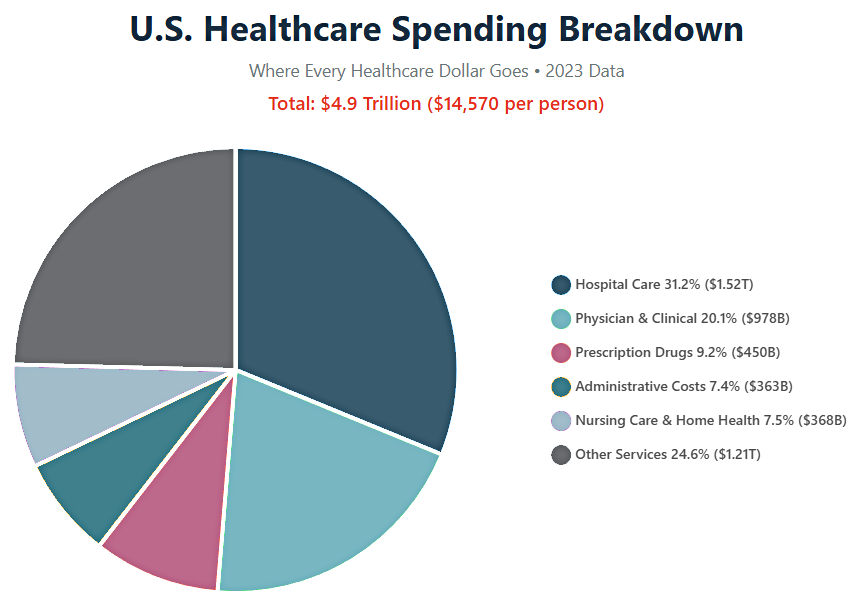
Sources: Peterson-KFF Health System Tracker, Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS), National Center for Health Statistics, Health Affairs Journal – 2023 Data
Hospitals that lead the charge in integrating home-based care can see these advantages:
· Extended reach and capabilities
· Integration of home services through expanded partnerships
· Succeed with value-based contracts
· Serve more patients across the care continuum
Value-Based Care’s Home-Centric Approach
Value-based care (VBC) fundamentally reshapes the care delivery landscape by changing the economic equation. Instead of paying for volume and utilization, value-based models provide fixed budgets to manage population health.This shift has profound implications for where and how care is delivered:
Financial incentives align with prevention: When providers bear financial risk, keeping patients out of hospitals becomes both an economic and a clinical priority.
Home becomes the default setting: Instead of bringing patients to care, value-based models focus on bringing care to patients.
Proactive outreach replaces reactive response: Rather than waiting for patients to deteriorate enough to require hospitalization, value-based care emphasizes ongoing monitoring and early intervention.
“What are the savings if a patient who would have been admitted five times can instead be admitted only twice?” Sullivan suggests this is a reasonable goal. “Even if it’s only reduced to three times, that is still a significant savings. Providing services to avoid complications because of technology in the home can make that happen.”
Evidence for Home-Based Care Success
The shift toward home-based care isn’t just theoretical. Existing models demonstrate their effectiveness:
Medicare Advantage Plans demonstrate a 43% reduction in avoidable hospitalizations compared to traditional Medicare. Recent research indicates this reflects a shift in care settings rather than purely based on improved outcomes.
Hospital at Home programs have demonstrated equivalent or better clinical outcomes compared to inpatient care for many conditions, along with higher patient satisfaction and lower costs.
Home-based primary care models for high-risk populations have shown reductions in emergency department visits, hospitalizations, and overall costs while improving quality of life.
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) reported these results from a pilot program:
The Home Health Value-Based Purchasing (HHVBP) model resulted in $14 million in annual savings and a 4.6% improvement in the quality of care.
Where will results like this take us in the future? McKinsey & Company estimates that as much as $265 billion worth of care services, representing up to 25% of the total cost of care for Medicare fee-for-service and Medicare Advantage beneficiaries, could shift from traditional facilities to the home without a reduction in quality or access.
Building Blocks of Effective Home-Based Care
Creating effective home-based care systems requires more than simply moving existing care practices into patients’ homes. Organizations need to develop integrated approaches that include:
1. Risk Stratification and Population Management
Effective home-based care begins with identifying which patients are most likely to benefit from home-based interventions. This requires:
- Predictive analytics to identify hospitalization risk
- Condition-specific criteria for home manageability
- Social determinants of health assessment
- Patient preference and caregiver availability evaluation
2. Technology-Enabled Monitoring
Home-based care requires extending clinical visibility beyond facility walls. As Sullivan notes: “Technology is what the whole system needs … in 2022 alone, 2.71 million Medicare patients received home health referrals.”
Effective monitoring solutions should:
- Provide continuous rather than episodic data
- Minimize burden on patients and caregivers
- Generate actionable insights rather than just raw data
- Alert clinicians to meaningful changes in patient status

3. Flexible Intervention Capabilities
Home-based care systems need multiple intervention options to address patient needs:
- Virtual visits for assessment and management
- In-home visits from appropriate clinical team members
- Medication adjustments and delivery
- Same-day diagnostics and treatments
- Temporary intensification of monitoring
4. Integrated Communication Systems
Effective home-based care requires seamless communication among all parties involved:
- Patients and family caregivers
- Primary care providers
- Specialists
- Home health agencies
- Pharmacy services
- Community support
When communication breaks down, patients often default to emergency services, undermining the home-based care model.
5. Clinical Workforce Development
Home-based care requires clinicians with specific skills and approaches:
- Comfort with remote assessment and decision-making
- Understanding of home environment challenges and resources
- Ability to partner effectively with patients and family caregivers
- Comfort with technology-mediated care
- Strong independent clinical judgment
As Sullivan observes: “The technology delivers all sorts of useful data. But unless healthcare workers are trained and expected to use it, the outcomes won’t change.”
Overcoming Barriers to Home-Based Care
Despite its advantages, shifting to home-based care models presents significant challenges:
Resistance: “Some organizations are fighting the switch,” Sullivan notes about resistance to care shifting outside hospital walls. “It’s understandable for systems with significant investments in facilities, but that won’t change the tide of care delivery.”
Reimbursement limitations: While payment models are evolving, many insurance plans still have limited coverage for home-based alternatives.
Technology integration challenges: Many existing healthcare technologies operate in silos, making it difficult to create truly integrated home-based care systems.
Clinical comfort levels: Providers trained in facility-based care often express concerns about managing patients remotely or in home settings.
Regulatory considerations: Home-based care models must navigate complex regulatory requirements, which are primarily designed for facility-based care.
Organizations leading in home-based care typically address these barriers through phased implementation, starting with specific populations where the case for home-based alternatives is strongest.
The Future of Home-Based Care
Looking ahead, several trends will likely shape home-based care evolution:
Integrated technology platforms that combine monitoring, communication, and intervention capabilities rather than standalone solutions.
Hybrid care models that blend virtual, in-home, and facility-based components based on clinical needs and patient preferences.
Specialized home-based programs for specific conditions like heart failure, COPD, and post-surgical recovery, with condition-specific protocols and technologies.
Expanded home diagnostics enabling more comprehensive assessment without facility visits.
AI-enhanced decision support to help clinicians interpret home-generated data and prioritize interventions.
The pace of this evolution will be determined largely by how quickly payment models shift to reward outcomes rather than utilization.
Getting Started with Home-Based Care
For organizations looking to develop or expand home-based care capabilities, consider these initial steps:
- Analyze current utilization patterns to identify areas where hospitalizations and ED visits may be preventable through enhanced home-based care.
- Assess your technology infrastructure to determine what capabilities you already have and identify the gaps that need addressing.
- Start with defined populations where you have existing relationships and clear clinical protocols.
- Build clinician comfort through education, shadowing, and gradual implementation.
- Partner strategically with technology companies and service providers that share your vision for home-based care.
Making the Shift to VBC in Your Organization
The shift from facility-centric to home-centric care represents one of the most significant transformations in healthcare delivery. As value-based care models continue to expand, organizations that develop robust home-based care capabilities will gain both clinical and economic advantages.
This shift doesn’t mean hospitals disappear—they are essential for certain types of care. Instead, it means that facility-based care is just one component of a broader care continuum centered around patients’ homes and daily lives.
By embracing this paradigm shift and developing the systems to support it, healthcare organizations can simultaneously improve patient experience, enhance clinical outcomes, and create more sustainable economic models. The future of healthcare is in the places patients call home.










